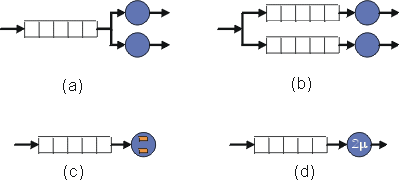
a. There are two operators available. The arriving customers are assigned by a so-called dispatcher to the next available operator. This principle is used at the check-in at the airport for example.
b. Here are two parallel servers available, too. But the clients are divided 50%/50% to the two queues at the time of arrival.
c. There is only one operator and one queue. But the operator can serve two customers simultaneously.
d. There is only one operator and one queue. But the operator works at double speed.