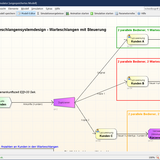
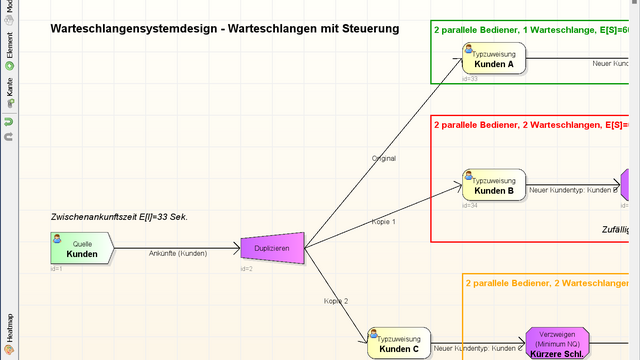
Simulation of a M/G/1 queue
The inter-arrival times of the customers are exponentially distributed, the distribution for the service times can be selected to be gamma distribution, exponential distribution and log-normal distribution. In the case of the exponential distribution this results in an M/M/ 1 queue.
At the bottom of the page the parameters of the inter-arrival and service time distributions can be adjusted. The ratio of service and the arrival rate defines the traffic rate.
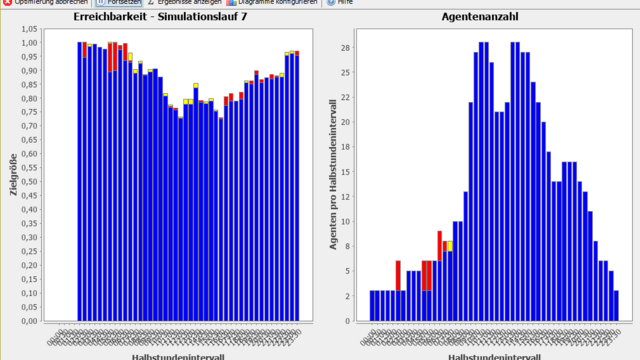
In the diagram the number of clients in the system at time t is specified. Each jump upwards defines a customer arrival, each jump to the bottom means the end of a service time. The service time are also denoted below.